2026
JupyterLab
JupyterLab is a modern, web-based interactive development environment for Python and other languages. It combines notebooks, terminals, file management, and interactive tools into one unified workspace.
Python Setup
To do symbolic calculation safely and high-quality numerical work, the most practical stack is:
Frequently Used Terminal Commands
macOS is built on Unix, which means powerful terminal commands are available for file management, networking, system monitoring, and development tasks.
pyenv
Pyenv is an essential tool for Python developers, especially when working on multiple projects that require different Python versions. It allows you to easily switch between versions and maintain project-specific environments without affecting your system Python. Some key benefits of using pyenv include:
- Manage multiple Python versions (3.8, 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 etc.)
- Maintain project-specific environments
- Avoid breaking system Python
- Ensure team-wide version consistency
Homebrew (brew)
Homebrew (brew) is the most popular package manager for macOS. It simplifies the installation, update, and management of software directly from the terminal. Instead of manually downloading .pkg or .dmg files, developers can install tools using a single command.
Linus Torvalds on AI, GPUs, and Kernel Development
Let’s take a look at Linus Torvalds’ thoughts on the hardware industry shift from CPUs toward GPUs and AI-driven accelerators, what that means for kernel development, and whether AI tools might ever replace real maintainers.
Tongue Twister Challenge Collection
Tongue twisters are powerful tools for improving pronunciation, clarity, confidence, and verbal agility. They are used by actors, teachers, news readers, debaters, podcasters, and language learners across the world. When sounds repeat rapidly, your brain and mouth must coordinate precisely. At first it feels messy. Then it becomes magic.
Complete India Post Route from Booking to Delivery
This is a real operational case study of how a Business Parcel moved across the India Post logistics network from origin to doorstep.
How to Predict Parcel Arrival with India Post Tracking
A parcel moving through the postal network follows structured procedures defined by departmental manuals, transport availability, and accountability rules. When you learn how scanning logic, routing hierarchy, and bag closures work, prediction becomes practical rather than emotional.
Gemini API and How to Use It
Artificial intelligence becomes truly powerful when it moves from a chat window into automation. Instead of manually asking questions, we can build programs that send thousands of requests, generate reports, prepare lecture notes, summarize books, or build datasets while we sleep. The bridge between an idea and such automation is the API key. Understanding how this key works, how it is protected, and how it is used inside real code is the first major step toward becoming an effective AI engineer.
Gemini Models: Pro, Flash, and Flash Lite
Modern releases differ in reasoning depth, speed, and operational price, and these dimensions determine whether a workflow remains experimental or becomes production grade.
Linear Algebra
Following is the detailed chapter-wise outline for the Linear Algebra book focused on physical applications.
Page Contents
Page Content Guide:
Vector Differentiation
Vector differentiation is the mathematical process of determining how vector quantities change with respect to a scalar variable, most commonly time or space, providing a precise language to describe motion, flow, and field variation in physics.
Hooke’s Law
Hooke’s Law is one of the foundational principles of classical mechanics and elasticity theory, describing the linear relationship between the force applied to an elastic body and the resulting deformation, provided the deformation remains within the elastic limit of the material. Formulated in the 17th century by the English scientist Robert Hooke, the law captures the essential behavior of springs, wires, rods, and a wide class of solid materials when subjected to small stresses. In its simplest and most widely used form, Hooke’s Law states that the restoring force developed in an elastic system is directly proportional to the displacement from its equilibrium position and acts in the opposite direction.
Scalar and Vector Products
Scalar (dot) and vector (cross) products are fundamental binary operations between vectors that yield, respectively, a scalar measuring directional alignment and a vector representing oriented area and rotational tendency, forming the mathematical backbone of geometry, mechanics, and field theory.
Vector Algebra
Vector Algebra is the mathematical framework that deals with quantities possessing both magnitude and direction and provides systematic rules for their representation, manipulation, and combination, forming the backbone of physical descriptions of space, motion, and fields.
Structure of Formal Salutation
The first and most crucial stage of any academic lecture or formal speech is the formal salutation. This is the point at which the speaker brings together the stage, the audience, and the occasion into a single coherent frame. A well-crafted salutation not only establishes the seriousness and tone of the speech but also creates a sense of discipline, attentiveness, and expectation among the listeners.
औपचारिक अभिवादन
किसी भी अकादमिक व्याख्यान या औपचारिक भाषण का पहला और सबसे महत्वपूर्ण चरण औपचारिक अभिवादन होता है। यह वह बिंदु है जहाँ वक्ता मंच, श्रोता और अवसर—तीनों को एक सूत्र में बाँधता है। सही ढंग से रचा गया अभिवादन न केवल भाषण की गंभीरता स्थापित करता है, बल्कि श्रोताओं में अनुशासन और अपेक्षा की भावना भी उत्पन्न करता है।
सेवानिवृत्ति भाषण: 2026
निम्नलिखित 31 जनवरी 2026 को इतिहास-कक्ष-1, एसकेएमयू दुमका में आयोजित डॉ. हस्मत अली और डॉ. संजय कुमार सिन्हा के सेवानिवृत्ति समारोह के दौरान प्रस्तुत किए गए सेवानिवृत्ति भाषणों के अंश हैं:
Talk on AI
In 1950, Alan Turing published a seminal paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” in which he asked the provocative question: “Can machines think?” This question laid the foundation for the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and has since sparked decades of research and debate.
Coherent States
There are several distinct definitions and constructions of coherent states in the literature, each with its own mathematical formulation, physical interpretation, and domain of applicability. Below are some of the most prominent types of coherent states, along with their definitions, mathematical formulations, descriptions, applications, and foundational references.
Upgrading an Old Jekyll Project to Jekyll 4: Full Error Diagnosis and Fix
This project was originally built using Jekyll 3.x and worked correctly for several years. Later, the local system Ruby environment was upgraded and Jekyll 4 was installed. This guide documents the complete process of diagnosing and resolving incompatibilities during the migration.
Quantum Information: NonG Measure
The non-Gaussianity (nonG) of a continuous-variable (CV) quantum state $ \rho $ is defined as the quantum relative entropy distance between $ \rho $ and a reference Gaussian state $ \rho_G $ that has the same first moments and the same covariance matrix as $ \rho $:
Quantum Information: Weigner Non-Gaussianity Measure
A celebrated phase-space description of nonclassicality in single-mode quantum oscillators is based on the presence of negative regions of the Wigner function.
Since the Wigner function is a normalized but not positive-definite quasi-probability distribution, its negativity has no classical counterpart.
2025
Franck Condon Principle
The Franck–Condon principle is one of the most fundamental concepts in molecular spectroscopy, explaining why vibrational structures appear in electronic spectra of molecules and why certain transitions are more intense than others. When a molecule undergoes an electronic transition—whether by absorption or emission of radiation—the change in the electronic state occurs on a timescale much faster than nuclear motion. Electrons are extremely light compared to nuclei; therefore, their transitions happen almost instantaneously relative to the vibrational and rotational movement of the nuclei. As a consequence of this difference in timescales, the nuclei can be considered “frozen” during the electronic transition. This approximation is the core of the Franck–Condon principle and leads to a vertical transition between potential energy curves on a Born–Oppenheimer energy diagram.
Scattering: Partial Wave Analysis
Partial wave analysis is a fundamental method in quantum scattering theory used to analyze the interaction of a particle with a localized potential by exploiting the rotational symmetry of the problem. When a quantum particle of definite momentum is incident on a scattering center, its wavefunction far from the interaction region can be expressed as a superposition of an incoming plane wave and an outgoing spherical wave.
Chokes and Transformers
Chokes and transformers are fundamental electromagnetic components widely used in electrical and electronic systems, particularly in power supplies, communication circuits, and signal-conditioning networks. Both devices operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction and magnetic flux linkage, yet they serve distinct functional roles within circuits. A choke is essentially an inductor designed primarily to impede alternating current (AC) while allowing direct current (DC) to pass with minimal resistance. In contrast, a transformer is a static electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through mutual induction, usually with the purpose of changing voltage or current levels, or providing electrical isolation.
RF and AF Oscillators
Oscillators are fundamental electronic circuits capable of generating periodic waveforms without the need for an external input signal. They operate by converting direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) signals through the use of active devices such as transistors, operational amplifiers, or vacuum tubes, in conjunction with passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Depending on the frequency range of the generated signal, oscillators are broadly classified into Audio Frequency (AF) oscillators and Radio Frequency (RF) oscillators. AF oscillators typically generate signals in the range of approximately 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which corresponds to the human audible spectrum. These oscillators are widely used in audio signal generators, public address systems, audio testing equipment, and musical instruments. RF oscillators, on the other hand, operate at much higher frequencies, typically from hundreds of kilohertz to several gigahertz, and form the backbone of radio communication systems, including transmitters, receivers, radar, television broadcasting, and wireless communication technologies.
Capacitors
A capacitor is a fundamental passive electronic component used to store electrical energy in the form of an electric field. It consists essentially of two conducting surfaces (plates) separated by an insulating medium known as a dielectric. When a potential difference is applied across the plates, equal and opposite charges accumulate on them, giving rise to an electric field within the dielectric. The ability of a capacitor to store charge per unit potential difference is quantified by its capacitance, measured in farads (F). Capacitors are indispensable in both DC and AC circuits and play a crucial role in signal processing, power conditioning, filtering, timing, coupling, decoupling, and energy storage.
Breadboard Usage
A breadboard is one of the most fundamental and widely used tools in experimental electronics and applied physics laboratories, especially at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels. It serves as a temporary construction platform for prototyping, testing, and analyzing electronic circuits without the need for soldering. The term “breadboard” originates historically from early experimental setups where wooden boards (sometimes literally breadboards) were used to mount electronic components. Modern breadboards, however, are standardized plastic boards with internal metallic spring contacts arranged in a highly structured manner.
JET: English-Lecture-VI
Clock
JET: English-Lecture-V
Calendars
UG Practicals
📘 List of Practicals
PG Practicals
SEM-II
Road Map: SUSY
🔷 Where You Stand (Important)
Contour Integration
The basic idea of contour integration is to extend the concept of integration from the real line to the complex plane. Instead of integrating a function along a real interval, we integrate it along a path (or contour) in the complex plane. This allows us to use the properties of analytic functions and the residues of poles to evaluate integrals that would be difficult or impossible to compute using standard real analysis techniques.
JET: English-PRACTICE SET-I
PRACTICE SET-I
JET: English-Lecture-IV
Ratio
Quantum Mechanics in Momentum Space by M Lieber
By M. Lieber Received 18 June 1974
JET: English-Lecture-III
Time & Distance
PG-II-Practical
Star & Delta Connection
Star (also called Wye or Y) and Delta (Δ) connections are fundamental network configurations used extensively in electrical engineering, circuit design, and power system analysis. These connections help simplify complex three-phase networks, making them easier to analyze for voltage, current, impedance, and power calculations. The star connection consists of three circuit elements whose one end is connected to a common junction known as the star point or neutral point, while the other ends form the three independent phase terminals. This configuration resembles the shape of the letter ‘Y’. It is widely used in power transmission systems, distribution networks, and balanced load connections due to its ability to provide two voltage levels—phase and line voltages.
JET: English-Lecture-II
Number & Letter Series
Fock
On the Theory of the Hydrogen Atom
by V. Fock, Leningrad
(Received August 5, 1935)
Fock-German
Theory of the Hydrogen Atom
JET - Paper-I
These topics will be covered from the subject General Paper on Teaching & Research Aptitude (Code No. 00, Paper-I), and the reading materials can be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinks.
JET: English-Lecture-I
Number System
JET: Lecture-V
1. Scalar and Vector Potentials
JET: Lecture-IV
Integral Theorems
JET: Lecture-III
Line, Surface and Volume Integral
Resistors
Resistors: Types, Characteristics, and Colour Coding
Frame Of Reference
In the study of scattering theory, nuclear reactions, and collision processes, the distinction between the Laboratory (Lab) reference frame and the Centre-of-Mass (CM) reference frame plays a central role. These two frames provide different perspectives for describing the motion, momentum transfer, and angular distribution of interacting particles. Since observations in an experiment are made in the laboratory frame, but theoretical simplicity often arises in the centre-of-mass frame, understanding the transformation between these two coordinate systems becomes essential.
Alpha Scattering
Alpha (α) scattering refers to the interaction of alpha particles—helium nuclei consisting of two protons and two neutrons—with atomic nuclei or atoms. The study of α-scattering has played one of the most pivotal roles in the development of modern physics. Historically, Rutherford’s α-scattering experiments in 1909 led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus and gave rise to the planetary model of the atom. These experiments showed that most α-particles pass through thin metal foils with little deflection, while a very small fraction undergo large-angle scattering, revealing the presence of a compact and massive nucleus.
3D Collision
The theory of collision in three dimensions is a fundamental aspect of quantum scattering, describing how a particle interacts with a potential when motion is not restricted to a single line but occurs in full three-dimensional space. Unlike one-dimensional scattering, where the particle approaches the potential from the left or right, three-dimensional collisions require the description of wave propagation in spherical geometry. This approach is crucial in understanding atomic, nuclear, and molecular processes where interactions occur isotropically.
Molecular Spectra
Rotational, Vibrational and Electronic Spectra of Diatomic Molecules
JET - Physical Science
These topics will be covered here, and the reading materials can be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinks.
UG Sem-I
MSC Sem-II
These topics will be covered here, and the reading materials can be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinks.
MSC Sem-I
JET-NET PAGE
UG & PG Page
Coding Page
Practical Question: Python
Numerical Methods Problem Set
Learning Objectives:
- Review all built-in, NumPy, and math functions used across typical numerical methods problems given at the end of this page.
- Understand and apply key numerical methods including root finding, interpolation, curve fitting, numerical integration, and solving ODEs.
- Practice basic numerical algorithms using Python.
Interaction of Solids with EM Field
Learning Objectives:
Polarons
In solid-state physics, polarons are quasiparticles formed due to the interaction of an electron (or hole) with the phonons (quantized lattice vibrations) in an ionic crystal. This interaction leads to a modification of the electron’s motion, as it becomes “dressed” with a polarization cloud of lattice distortion.
Polaritons
In solid-state physics, polaritons are quasiparticles arising from the strong coupling of photons with optical phonons in a crystal. These coupled modes play a central role in understanding the optical properties of ionic crystals, particularly in the infrared frequency range.
Tight-Binding Approximation
Nearly Free Electron Model and Energy Bands in One Dimension, Tight-Binding Approximation
Small Oscillations
Small Oscillations, Normal Modes of Vibration, Coupled Oscillators
Poisson Bracket, Poisson Theorems
Learning Objectives:
Plasma Oscillations and Plasmons
Learning Objectives:
Hamilton–Jacobi Equation
Hamilton–Jacobi Equation with Example of Harmonic Oscillator
Generating Function
Learning Objectives:
Legendre Transformation
Learning Objectives:
Hamilton Equation of Motion
Hamilton’s Equations of Motion
Hamilton’s Principle
Hamilton’s Principle
Least Action Principle
The Principle of Least Action
Calculus of variation
Calculus of variation
Lagrange’s Equation
D’Alembert’s Principle, Lagrange’s Equation and Its Simple Applications
Dielectric Properties of Materials
Macroscopic Dielectric Constant
Numerical Methods
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors play a central role in linear algebra, with wide applications in physics, engineering, and data science. They help understand the action of a linear transformation in a given vector space.
Image Processing: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
🧠 Objective
This lecture explores the application of eigenvalues and eigenvectors in image processing using Principal Component Analysis (PCA). We will:
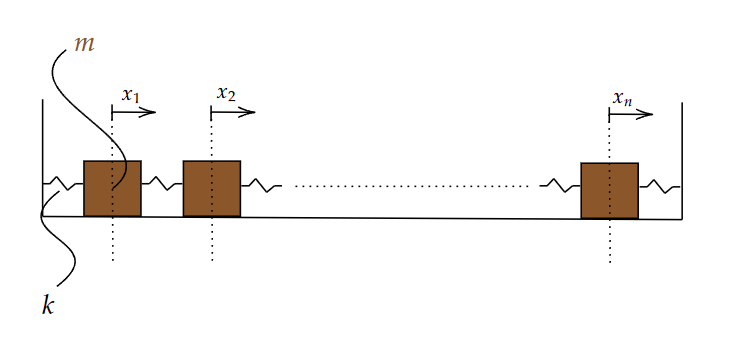
Dissertation: N-Interconnected Mass-Spring System
Dissertation-Heat Equation
Simulation of the Heat Equation in a Rectangular Room
Dissertation-Wave Equation
Simulation of the Wave Equation in a Circular Domain Using Python
Python: Course Contents
🚀 Hands-on Practice: Practice coding by clicking on button below:
Python: Object-Oriented Programming
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming style that organizes code into objects, which store data and perform actions. This method makes programs more structured, reusable, and secure. The four main concepts of OOP are:
Windows: Basics of Command Prompt
The Command Prompt (cmd.exe) is a command-line interpreter in Windows that allows users to execute commands, run scripts, and perform administrative tasks.
Basic Electronics: Boolean Algebra
Boolean algebra is a mathematical structure used to perform operations on binary variables (0s and 1s). It is fundamental in digital logic design and computer science.
The Concept of Isospin
Isospin is a quantum number that describes the symmetry between particles with similar properties but different electric charges. It was first proposed by Werner Heisenberg in 1932 to explain the near-degeneracy of protons and neutrons. These particles, collectively called nucleons, were found to behave similarly under the strong nuclear force, suggesting an underlying symmetry.
Assignment-I
Instructions:
Explain how complex physical expressions can simplify to exponential decay through Taylor series or other approximations. Provide detailed derivations for the following cases.
Quantum Tunneling
In this article we will study:
Scattering Revisited
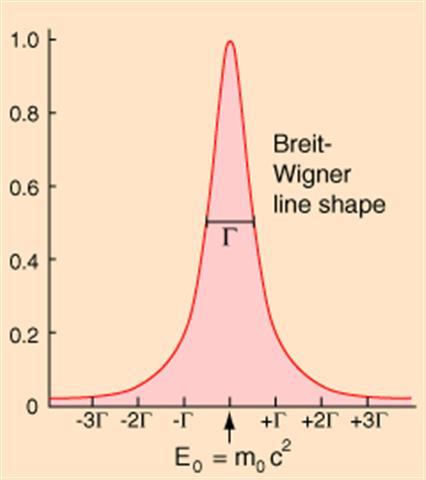
In this lecture, we will start by revisiting the basics of quantum scattering, focusing on partial wave analysis and phase shifts. The graph at the top illustrates the Breit-Wigner resonance curve, which we will discuss in detail after exploring resonance scattering and its role in energy-dependent cross-sections.
2024
Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear reactions can occur when a target nucleus $X$ is bombarded by a particle $a$, resulting in a daughter nucleus $Y$ and an outgoing particle $b$:
Basic Electronics: Semiconductors
In 1839, Becquerel discovered that some materials generate an electric current when exposed to light. This is known as the photoelectric effect and is the basis of operations of solar cells. Solar cells are made of semiconductors.
- Note: Semiconductors are materials that act as insulators at low temperatures, but as conductors when energy or heat is available.
Particle Physics: Quarks
Particle Physics: Conservation Laws
The conservation laws of energy, momentum, and charge govern all processes. In particle physics, additional empirical conservation laws are also crucial. They are:
- Conservation of baryon number
- Conservation of lepton number
- Conservation of strangeness
- Conservation of isospin
- Conservation of electric charge
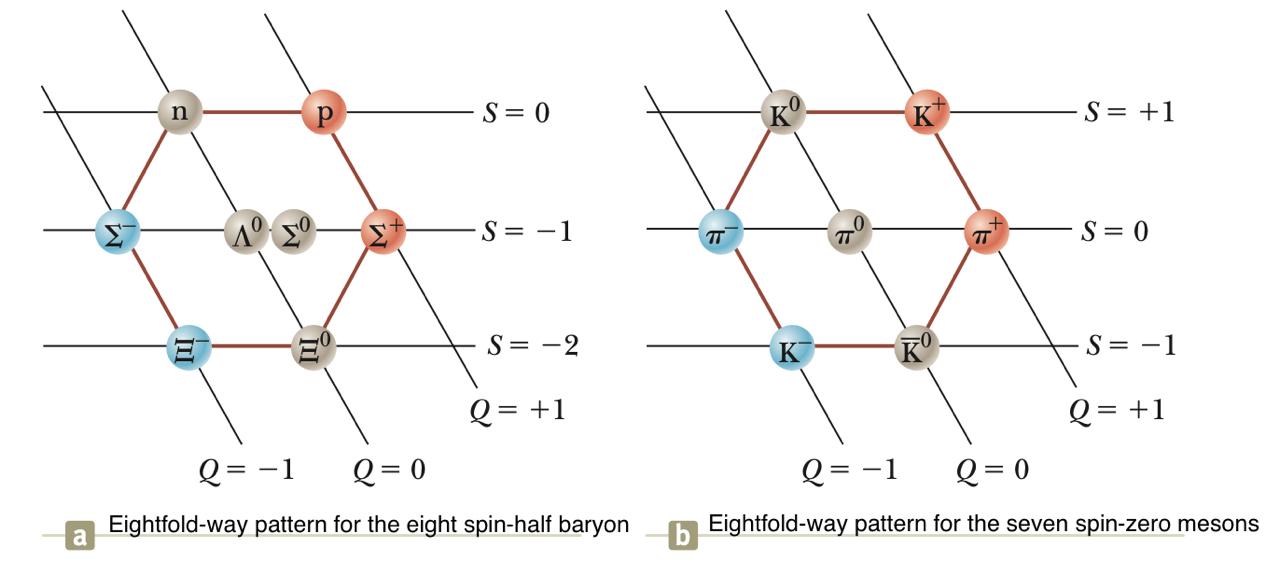
Particle Physics: Particle Classification
Japanese physicist Hideki Yukawa proposed in 1935 that the nuclear force is mediated by a new particle, a meson, whose exchange between nucleons causes the force. He predicted its mass to be about 200 times that of an electron, earning him a Nobel Prize in 1949. Because the new particle would have a mass between that of the electron and that of the proton, it was called a meson (from the Greek meso, “middle”)
Particle Physics Introduction
PG-III Lecture Topics
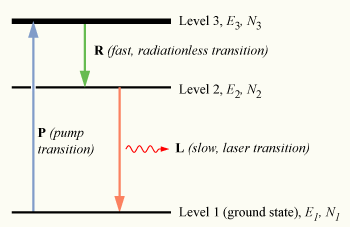
LASER Rate Equation
Stark Effect in Hydrogen Atom
In the hydrogen atom, the energy levels are determined by the principal quantum number \(n\), and for a given \(n\), the energy is given by:
Approximation Method
Perturbation theory is a powerful tool in quantum mechanics used to study systems where the Hamiltonian can be separated into a known part \(H_0\) and a small perturbation \(H'\). The goal is to find approximate solutions to the Schrödinger equation for the full Hamiltonian \(H = H_0 + H'\) by treating the perturbation as a small correction to the known system.
Scattering
Consider the Hamiltonian $H$ of the system, which is time-independent, given by
Derivations-QM: Current Density Conservation Equation
The Dirac equation for a free particle is given by:
LASER
``` Basic principles and different LASER’s: principles and working of Ruby Laser, He-Ne Laser, Solid state laser, semiconductor laser CO2 LASER and qualitative description of longitudinal and TE- LASER systems, Excimer LASER, Dye LASER, Roman LASER, Plasma recombination LASER.
Tutorial-QM
This tutorial covers Klein-Gordon and Dirac equations in quantum mechanics.
Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
Below is the outline of the lecture on Relativistic Quantum Mechanics, covering the Klein–Gordon equation, Dirac equation, probabilities and current densities, magnetic moment and spin of the electron, and free particle solutions of the Dirac equation.
Additional Resources
Science
1. What is Science?
2022
Back to Top ↑2021
KaTeX demo
Including mathematical notations in your post is possible thanks to KaTeX.
To add a math notation all you need to do is add $$ signs at the beginning and end of the notation.
An example for you guys,
Mermaid demo
Want to add diagrams, charts and visualizations in your post?
It is possible and guess what? It’s not that difficult thanks to Mermaid.
All you need to keep in mind is you’ll have to wrap your Mermaid markup in a div with class mermaid.
Here is a simple example of a basic flowchart,
2020
Google Docs + LaTeX on Mobile
🎯 Learning Objectives:
Dissertation
Technical Skills
Introduction to ADB (Android Debug Bridge)
🎯 Learning Objectives
2017
Jekyll Remote Theme Support Added
Basically Basic can now be installed remotely for use on GitHub Pages!
2013
Markup: Syntax Highlighting
Post displaying the various ways one can highlight code blocks with Jekyll. Some options include standard Markdown, GitHub Flavored Markdown, and Jekyll’s {% highlight %} tag.
Markup: HTML Elements and Formatting
A variety of common HTML elements to demonstrate the theme’s stylesheet and verify they have been styled appropriately.
Markup: Image Alignment
The best way to demonstrate the ebb and flow of the various image positioning options is to nestle them snuggly among an ocean of words. Grab a paddle and let’s get started.
Markup: Text Alignment and Transformations
Sample text to demonstrate alignment and transformation classes.
Markup: Title with Special — Characters
Putting special characters in the title should have no adverse effect on the layout or functionality.
Markup: Title with Markdown
Using Markdown in the title should have no adverse effect on the layout or functionality.
2012
Markup: Text Readability Test
A large amount of sample text to test readability of a text heavy page.
Layout: Hero Image
This post should display a large hero image at the top of a page.
Layout: Excerpt (Generated with Separator Tag)
This is the post content. Archive-index pages should display an auto-generated excerpt of all the content preceding the excerpt_separator, as defined in the YAML Front Matter or globally in _config.yml.
Be sure to test the formatting of the auto-generated excerpt, to ensure that it doesn’t create any layout problems.
Layout: Excerpt (Defined)
This is a user-defined post excerpt. It should be displayed in place of the auto-generated excerpt or post content on index pages.
Layout: External Hero Image

This post should display a large hero image at the top of a page.
2010
Post: Twitter Embed
Oh I dunno. It's probably been over 15 years since I smudged out a face with a pencil and kneaded eraser. #WIP #Sktchy pic.twitter.com/PwqbMddyVK
— Michael Rose (@mmistakes) February 1, 2017
Post: Video (YouTube)
Post: Quote
Only one thing is impossible for God: To find any sense in any copyright law on the planet.
Post: Standard
All children, except one, grow up. They soon know that they will grow up, and the way Wendy knew was this. One day when she was two years old she was playing in a garden, and she plucked another flower and ran with it to her mother. I suppose she must have looked rather delightful, for Mrs. Darling put her hand to her heart and cried, “Oh, why can’t you remain like this for ever!” This was all that passed between them on the subject, but henceforth Wendy knew that she must grow up. You always know after you are two. Two is the beginning of the end.
Mrs. Darling first heard of Peter when she was tidying up her children’s minds. It is the nightly custom of every good mother after her children are asleep to rummage in their minds and put things straight for next morning, repacking into their proper places the many articles that have wandered during the day.
Post: Modified Date
This post has been updated and should show a modified date if last_modified_at is used in the layout.
2009
Suspicio? Bene … tunc ibimus? Quis uh … CONEXUS locus his diebus? Quisque semper aliquid videtur, in volutpat mauris. Nolo enim dicere. Vobis neque ab aliis. Ego feci memetipsum explicans. Gus mortuus est. Lorem opus habeo. Jackson Isai? Tu quoque … A te quidem a ante. Vos scitis quod blinking res Ive ‘been vocans super vos? Et conteram illud, et conteram hoc. Maledicant druggie excors. Iam hoc tu facere conatus sum ad te in omni tempore? Ludum mutavit. Verbum est ex. Et … sunt occid
Check for long titles and how they might break layouts.
Antidisestablishmentarianism
This post title has a long word that could potentially overflow the content area.
Edge Case No Yaml Title
This post has no title specified in the YAML Front Matter. Jekyll should auto-generate a title from the filename.
Edge Case: No Body Content
This post has no body content and should be blank on the post’s page.
Edge Case: Many Categories
This post has many categories.
Edge Case: Many Tags
This post has many tags.
Edge Case: Nested and Mixed Lists
Nested and mixed lists are an interesting beast. It’s a corner case to make sure that lists within lists do not break the ordered list numbering order and list styles go deep enough.